Have you ever wondered how airplanes store fuel safely during flight? It’s a critical question that affects the lives of millions of passengers every day.
The aviation industry has developed a range of ingenious solutions to ensure that fuel is stored securely and efficiently in planes, from strategically placed fuel tanks to advanced monitoring systems.
In this blog post, we’ll explore the world of aircraft fuel storage, exploring the design, engineering, and safety protocols that keep fuel contained and passengers protected.
You’ll gain a new appreciation for the incredible technology and expertise that goes into every flight. Join us as we dive deep into an airplane’s heart and uncover the secrets of fuel storage safety.
Prepare for an eye-opening journey that will change your thoughts about flying.
Essential Components of Aircraft Fuel Storage
| Material | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Aluminum Alloys | – Lightweight, reducing overall aircraft weight | – Prone to corrosion, requiring frequent maintenance |
| – High strength-to-weight ratio | – Less flexibility compared to composites; can dent or warp | |
| – Economical due to easier machining and abundance | – Conductive, potentially increasing the risk of lightning impact | |
| – Proven track record in aerospace applications | ||
| Composite Materials | – Excellent corrosion resistance | – More expensive to produce and repair |
| – Greater flexibility allows for more complex shapes | – More sensitive to impact damage and can be harder to detect | |
| – Lighter than aluminum, providing further weight savings | – Requires advanced technologies for manufacturing | |
| – Non-conductive, reducing risks associated with lightning | – Longer development time for new tank designs |
At the heart of every airplane lies a complex system responsible for safely storing and managing fuel, the lifeblood of flight.
Aerial vehicles rely on three primary components—fuel tanks, fuel lines, and sealing systems—to ensure the utmost safety and efficiency.
Fuel tanks are sturdy reservoirs that securely hold the plane’s fuel supply. They are carefully designed to withstand the various stresses encountered during flight.
These tanks work in tandem with a network of fuel lines that transport the fuel from the tanks to the engines, regulated by pumps, valves, and filters along the way.
Sealing systems prevent leaks and contamination, ensuring fuel remains contained within the tanks and lines.
The seamless integration and proper maintenance of these components are vital to maintaining the integrity of the fuel storage system and the overall safety of the aircraft.
In the following sections, we will examine each of these essential components in more detail, exploring their design, materials, and the cutting-edge technologies that keep them functioning at the highest level.
Safety Protocols and Procedures for Handling Fuel in Airplanes
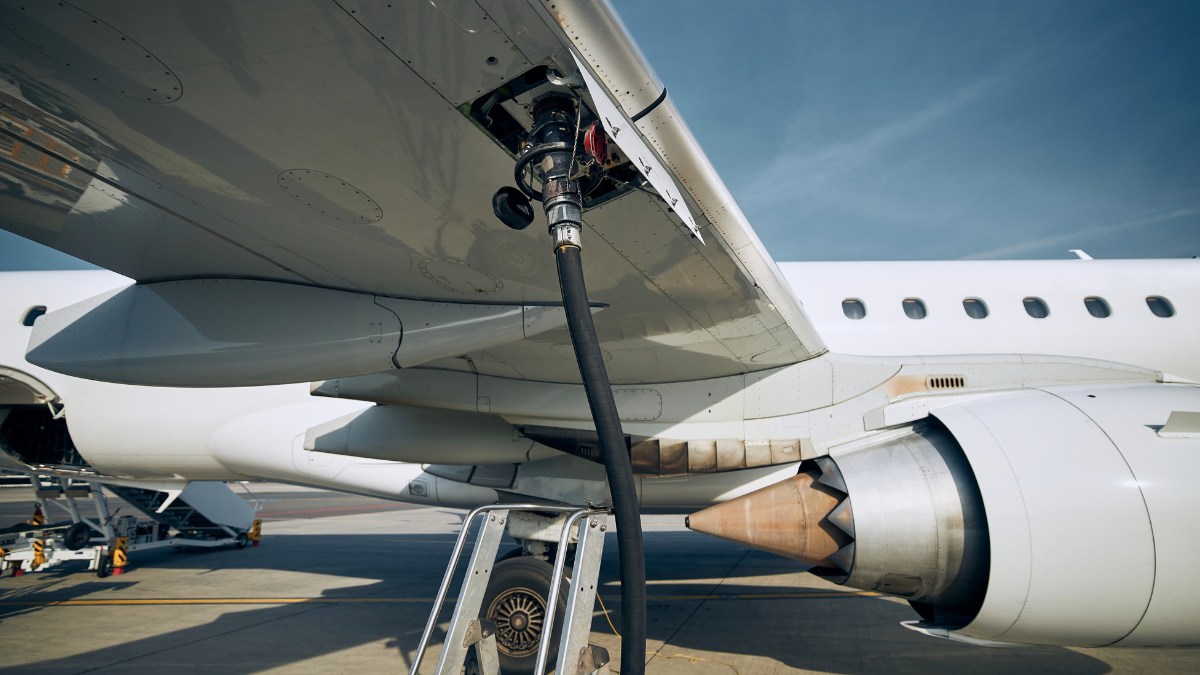

Detailed protocols and procedures must be followed religiously to minimize risks and ensure compliance with aviation standards.
Look closely at some key protocols that keep fuel management safe and efficient.
1. Fuel Handling Procedures
Fueling and refueling an aircraft is a delicate process that requires strict adherence to standard operating procedures (SOPs).
These SOPs cover every aspect of the process, from the initial grounding and bonding of the aircraft to the final checks and documentation.
Grounding and bonding techniques are particularly critical, as they prevent the build-up of static electricity, which could potentially ignite fuel vapors.
Connecting the aircraft, fuel truck, and fueling equipment to a common ground safely dissipates any static charges.
2. Fuel Quality Control
The purity of the fuel is another crucial factor in maintaining safety.
Contaminated fuel can lead to engine failures and other hazards, making quality assurance measures essential.
Regular testing and monitoring of fuel samples help identify impurities or inconsistencies, ensuring that the fuel meets aviation authorities’ stringent standards.
These tests check for water content, particulate matter, and other contaminants that could compromise fuel quality.
3. Fueling Equipment Maintenance
Fueling equipment must be kept in top condition to mitigate risks through regular maintenance routines further.
Hoses, nozzles, and other components are inspected frequently for signs of wear, damage, or leaks.
Any equipment that fails to meet the high safety standards is promptly replaced to prevent malfunctions that could lead to fuel spills or other incidents.
By diligently following these protocols and prioritizing safety at every step, the aviation industry maintains an impressive record of fuel management safety.
In the next section, we’ll explore some real-world applications and case studies that demonstrate the importance of these protocols in action.
4. Advanced Fuel Storage Safety Systems
“Aviation technology is constantly advancing, leading to innovative safety systems that safeguard aircraft and passengers.
This section highlights key technological advancements enhancing fuel storage safety in aviation.
5. Inerting Systems
A pivotal advancement in aviation safety, fuel tank inerting systems significantly mitigate combustion risks.
These systems inject inert gases like nitrogen into fuel tanks, displacing oxygen and dramatically reducing fire risks during lightning strikes or electrical faults.
These inerting systems, common across various aircraft, are essential for maintaining a non-flammable environment within the fuel tanks, which is crucial under all operating conditions.
6. Ventilation Systems
Integral to fuel safety, modern aircraft’s ventilation systems ensure proper air pressure and prevent vapor accumulation, which could lead to fires.
These systems, comprising a sophisticated network of vents, valves, and pressure regulators, adhere to stringent safety standards.
They regulate air pressure and prevent contaminants from compromising fuel quality by employing advanced filtration technologies.
Both systems showcase the industry’s commitment to enhancing safety through technological innovation, significantly lowering the risk of fuel storage-related incidents and setting new standards in aviation safety protocols.”
7. Fuel Quantity Indication Systems (FQIS)
Accurate fuel measurement is essential for both flight planning and in-flight fuel management.
Fuel Quantity Indication Systems (FQIS) use advanced sensors and gauges to provide pilots and ground crew real-time information on fuel levels, allowing for precise monitoring and decision-making.
FQIS technology has come a long way in recent years, with modern systems offering unprecedented accuracy and reliability.
These systems often integrate with other aircraft systems, such as the flight management system and the engine control units, to provide a comprehensive overview of the aircraft’s fuel status.
Some of the latest advancements in FQIS technology include digital interfaces, which provide pilots with easy-to-read displays and automated alerts for low-fuel situations.
These features enhance safety and operational efficiency, allowing pilots to make informed decisions quickly and accurately.
The combination of fuel tank inerting systems, advanced ventilation systems, and state-of-the-art fuel quantity indication systems has revolutionized how we approach fuel safety in modern aviation.
As technology progresses, we can expect to see even more innovative solutions that will further enhance the safety and efficiency of aircraft operations.
From integrating artificial intelligence to developing predictive analytics, the future of aviation fuel safety looks brighter than ever.
Case Studies and Incident Analyses: Fuel Storage
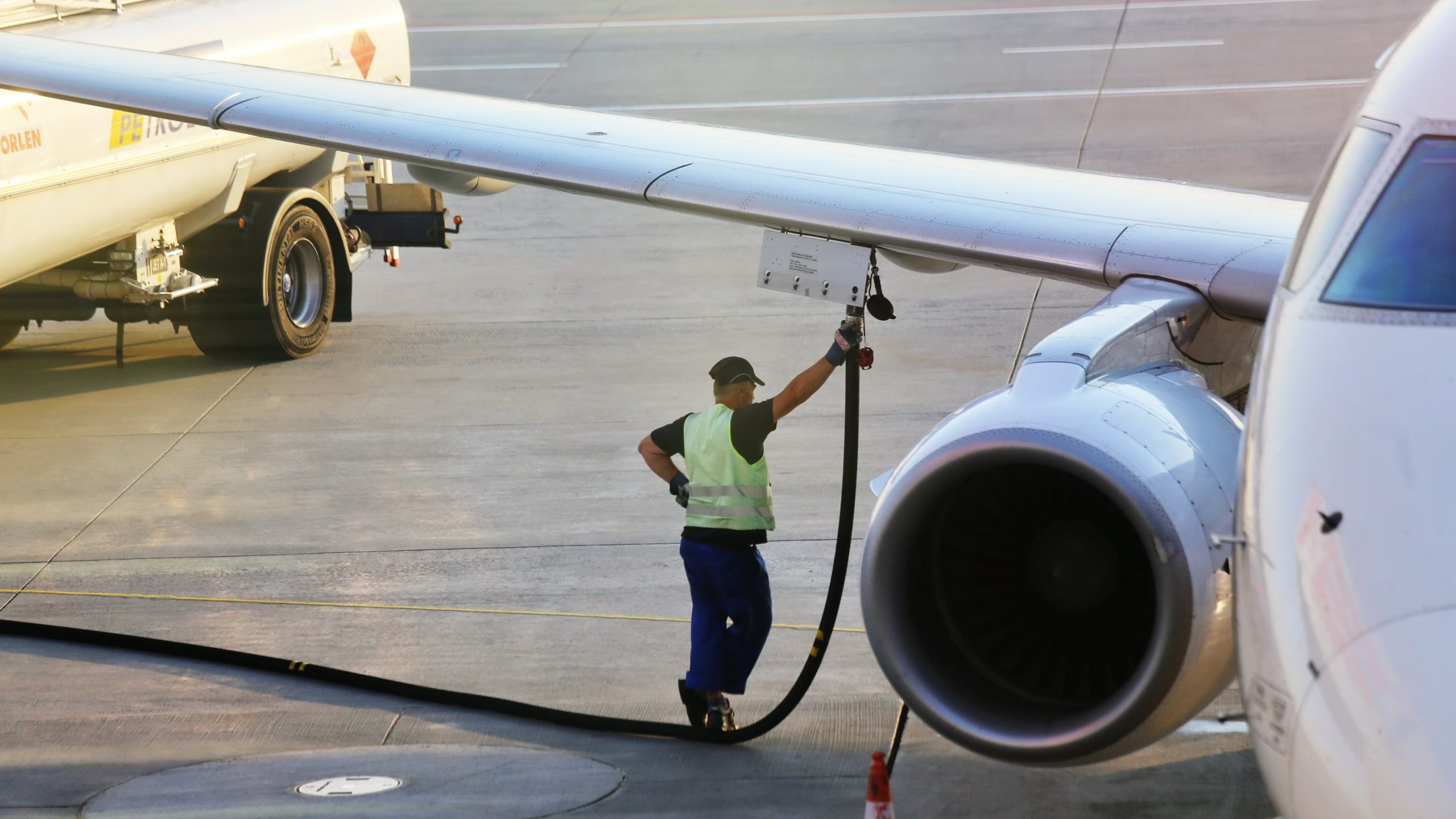

Throughout aviation history, incidents related to fuel storage have served as stark reminders of the importance of safety protocols and the need for continuous improvement.
The industry has made significant strides in enhancing fuel storage safety by analyzing past events and applying the lessons learned.
This section will explore some notable case studies and discuss emerging innovations.
1. Historical Incidents
One of the most infamous incidents related to fuel storage failures occurred in 1990 when a Philippine Airlines Boeing 737 exploded on the tarmac due to a fuel leak.
- The investigation revealed that a faulty fuel valve had allowed fuel to leak into the cargo hold, creating a volatile atmosphere ignited by a spark from a damaged electrical cable.
- This incident highlighted the need for more stringent maintenance checks and improved leak detection systems.
- Another significant case involved fuel contamination at a major international airport.
- The investigation found that a faulty filtration system had allowed water and debris to mix with the fuel, leading to several flight delays and cancellations.
- This incident prompted a review of fuel handling procedures and the implementation of more rigorous quality control measures.
These cases, among others, have underscored the critical importance of regular maintenance, effective monitoring systems, and swift response protocols in preventing fuel storage-related incidents.
2. Recent Advances in Safety
In response to these historical incidents, the aviation industry has developed and implemented a range of technological innovations and improved protocols to enhance fuel storage safety.
- One notable advancement is electronic fuel monitoring systems, which provide real-time data on fuel quality, quantity, and temperature.
- These systems can quickly detect anomalies or potential contaminants, allowing for swift corrective action.
- Many modern aircraft now feature inerting systems that replace oxygen in fuel tanks with inert gas, significantly reducing the risk of combustion.
- Alongside these technological innovations, international safety protocols have been updated to mandate more stringent fuel handling and storage procedures.
- These protocols cover every aspect of the fuel storage process, from initial receipt and testing to final dispensing into aircraft.
- Ground staff and engineers undergo extensive training to ensure they are well-versed in these protocols and can respond effectively to potential issues.
The impact of these advances has been significant, with a marked reduction in fuel storage-related incidents over the past few decades.
Industry data shows that implementing these new technologies and protocols has helped prevent countless potential disasters, ensuring safer air travel for millions of passengers worldwide.
3. Synthesis and Future Directions
The case studies and innovations discussed in this section underscore the importance of learning from past incidents and continually striving to improve fuel storage safety.
By analyzing historical events and applying the lessons learned, the aviation industry has developed and implemented effective solutions that have greatly enhanced safety.
However, the work is far from finished.
As air travel continues to grow and evolve, so must our approach to fuel storage safety.
Ongoing research and development in advanced leak detection, autonomous monitoring systems, and eco-friendly fuel alternatives promise to revolutionize the industry.
Ultimately, the key to ensuring the highest standards of fuel storage safety lies in a commitment to continuous improvement and vigilance.
By staying abreast of the latest technological advancements, adhering to stringent protocols, and fostering a culture of safety at every level, the aviation industry can continue providing the safest possible travel experience for passengers worldwide.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the safety measures for storing fuel in airplanes is crucial for ensuring the well-being of passengers, crew, and the aircraft itself.
From the strategic design of fuel tanks to implementing advanced safety systems and stringent regulations, every aspect of fuel storage plays a vital role in maintaining the highest aviation safety standards.
By studying historical incidents and applying the lessons learned, the industry has made significant strides in mitigating risks and preventing fuel-related accidents.
As technology evolves, so must our approach to fuel storage safety.
Through ongoing research, innovation, and a commitment to best practices, we can continue to provide the safest possible air travel experience for generations to come.
Together, let us remain vigilant in upholding these safety standards, ensuring the skies remain as safe as ever.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are The Most Common Causes of Fuel Storage Failures in Aircraft?
Common causes of fuel storage failures include leaks, corrosion, faulty seals, and inadequate maintenance.
How have Fuel Storage Safety Measures Evolved Over the Past Decade?
Over the past decade, fuel storage safety has improved through advanced monitoring systems, improved maintenance protocols, and the implementation of inerting systems.
What Technologies are Currently Being Used to Improve Fuel Storage Safety in Aviation?
Current technologies for fuel storage safety include electronic fuel monitoring, inerting systems, advanced leak detection, and improved tank materials.
Can you Explain the Role of Inerting Systems in Preventing Fuel Tank Explosions?
Inerting systems prevent fuel tank explosions by replacing oxygen with inert gas, reducing the risk of combustion.
What are the Standard Protocols for Handling a Fuel Storage Emergency in Aviation?
Standard protocols for fuel storage emergencies include shutting off the fuel supply, evacuating the area, notifying emergency services, and following established emergency response procedures.