Texas’ housing affordability is a hot topic, but what’s driving the trends? Many factors come into play, from demographics to income levels.
However, one crucial aspect often overlooked is geography. Location within the state can greatly impact the accessibility and cost of housing for Texans.
This article examines how the Lone Star State’s diverse landscapes and urban development patterns shape the housing market, creating unique challenges and opportunities for residents seeking affordable homes.
Join us as we uncover the compelling connections between geography and housing affordability in Texas, shedding light on a complex issue that affects millions of lives.
Texas’ Population Growth and Demographic Changes
Texas has experienced rapid population growth over the past decade, adding more people than any other state in the U.S.
The major sources of population increase include migration from other states and natural growth.
The state’s population is projected to reach between 36 and 44 million people by 2060, with most of the growth driven by domestic migration.
Demographic changes in Texas include age, ethnicity, and household composition shifts.
Hispanics are the largest population group in Texas and will be the largest racial/ethnic group in every age category by 2050.
The fastest-growing age groups are among people 65 years and older, with the number of people 65+ expected to increase by more than 88% between 2023 and 2050.
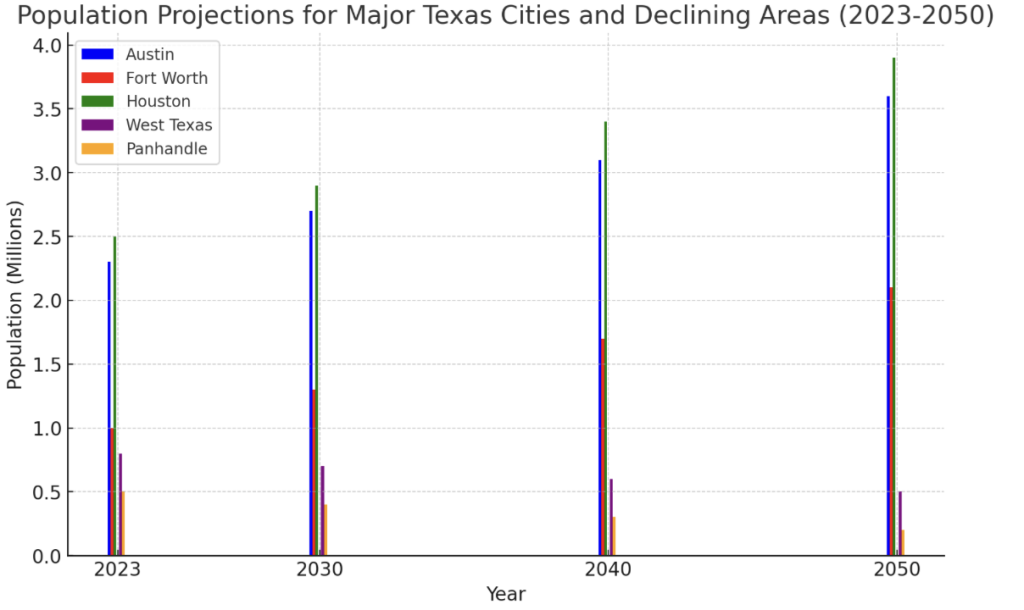
Migration trends show that major cities in Texas, such as Austin, Fort Worth, and Houston, are experiencing significant population growth, while many cities in west Texas and the Panhandle area are losing population.
The so-called “Texas Triangle” now holds 68% of the state’s 30.3 million residents.
The impact of demographic shifts on public services, infrastructure, and labor markets is significant.
Fast growth can cause challenges, such as pressure on infrastructure and increased housing costs, while counties losing population may face a lack of infrastructure and access to services.
However, the growth is generally good for the economy, as migrants are usually younger, more likely to be in the labor force, and more likely to be employed.
Texas’ population growth and demographic changes are characterized by rapid population growth, migration from other states, shifts in age and ethnicity, and significant impacts on public services, infrastructure, and labor markets.
Economic Factors Affecting Housing Affordability
1. General Impact on Affordability
Varying income levels significantly affect Texans’ ability to secure affordable housing. Higher earners can more easily absorb rising costs, while lower-income residents often struggle to keep pace.
2. Regional Income Comparisons
Striking disparities exist between urban and rural areas and among major cities. For example, the typical household in Austin earns $34,950 annually, far less than the state median of $54,727.
3. Economic Opportunities
The presence of major industries and job availability heavily influence housing prices and living standards. Cities with thriving economies, like Houston’s Energy Corridor, often see higher costs, while struggling areas may have more affordable but less desirable housing.
Geographical Factors Affecting Housing Affordability
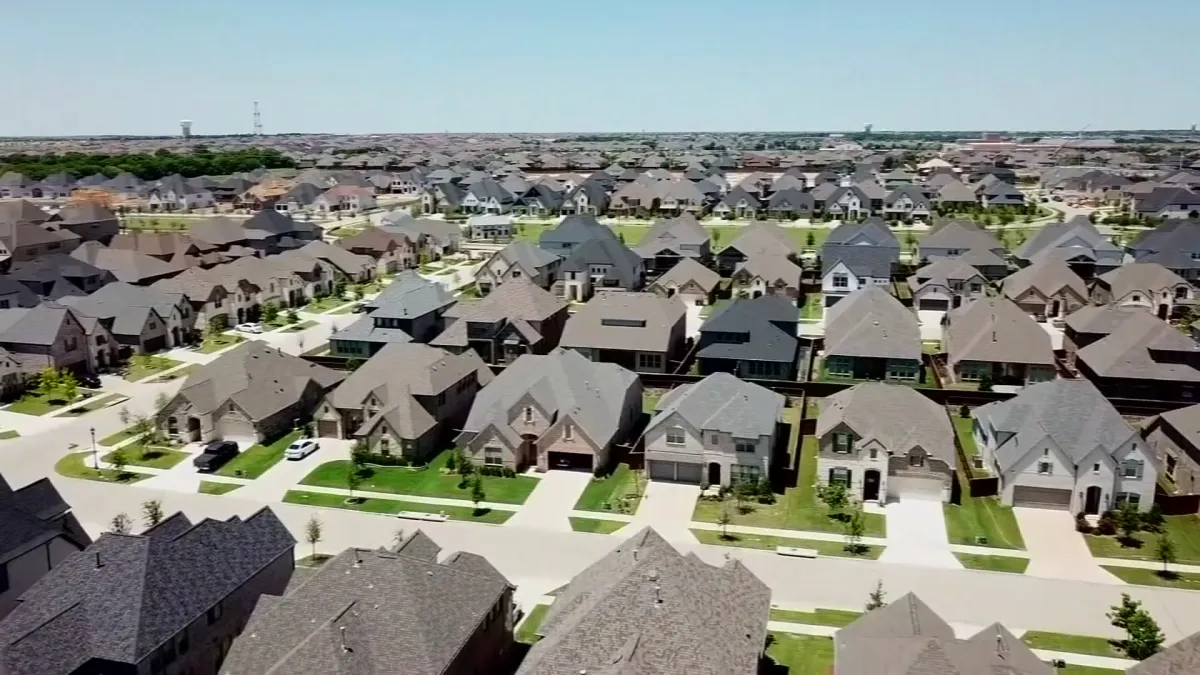
- Texas’ varied landscapes, from coastal plains to hill country, shape where and how development occurs. Flat, accessible areas enable sprawl, while more challenging terrains limit growth.
- Geography can constrain development, such as in flood-prone Houston, or allow for expansion, as seen in the sprawling Dallas-Fort Worth metroplex.
Environmental Concerns Affecting Housing Affordability
Climate change and its associated environmental impacts pose significant challenges to housing affordability and accessibility in Texas, particularly in areas vulnerable to natural disasters such as flooding, hurricanes, and extreme heat.
1. Rising Sea Levels and Coastal Erosion
- Rising sea levels threaten coastal communities, potentially displacing residents and damaging infrastructure.
- Coastal erosion can lead to the loss of land and property, affecting housing availability and affordability.
2. Increased Frequency of Extreme Weather Events
- More frequent and severe hurricanes, storms, and flooding can damage homes and infrastructure, leading to displacement and increased housing costs.
- Prolonged droughts and extreme heat can strain water resources and energy grids, impacting housing habitability and affordability.
3. Flood-Prone Regions
- Recurring flooding events can damage homes, leading to costly repairs and rebuilding efforts.
- Flood insurance premiums may increase, increasing housing costs and challenging affordability.
4. Coastal Communities Vulnerable to Hurricanes
- Hurricanes can cause widespread damage to homes and infrastructure, displacing residents and driving up housing costs
- Post-disaster rebuilding efforts may prioritize higher-end developments, further exacerbating affordability issues
Major Texan Cities
1. Houston
Economic Factors Affecting Housing Affordability
- Economic factors such as job growth, income levels, and housing supply and demand dynamics influence Houston’s housing affordability.
- The city’s economy, driven by energy, healthcare, and aerospace industries, impacts residents’ ability to afford housing.
Geographical constraints and opportunities
- Houston faces challenges like flooding due to its flat topography and proximity to the Gulf of Mexico.
- However, the city’s vast land area provides opportunities for expansion and development, which can impact housing availability and affordability.
2. Dallas
Impact of Income Disparities on Housing Access
- Income disparities in Dallas affect housing access, with lower-income residents facing challenges in finding affordable housing.
- The city’s economic growth has led to rising housing costs, exacerbating the issue of housing affordability for many residents.
Role of Urban Sprawl in Shaping Housing Markets
- Dallas’ urban sprawl has influenced housing markets by spreading development across a wide area, impacting commute times and housing prices.
- The expansion of suburbs has contributed to the city’s housing market dynamics and affordability challenges.
3. Austin
Gentrification’s Impact on Long-Term Residents
- In Austin, gentrification has led to long-term resident’ displacement as property values rise and neighborhoods undergo redevelopment.
- The influx of higher-income residents has transformed neighborhoods, affecting housing affordability and community dynamics.
Balancing Urban Expansion with Affordability
- Austin faces the challenge of balancing urban expansion with maintaining affordable housing options for residents.
- The city’s rapid growth and development have pressured housing affordability, requiring strategic planning to address the issue.
4. San Antonio
Affordable Housing Initiatives
- San Antonio has implemented various affordable housing initiatives to address housing affordability issues for its residents.
- These initiatives aim to provide housing options for low and moderate-income individuals and families, contributing to the city’s housing affordability landscape.
Geographical Advantages Impacting House Costs
- San Antonio’s geographical advantages, such as its central location in Texas and access to natural amenities, can impact housing costs.
- Factors like proximity to employment centers, transportation infrastructure, and desirable neighborhoods influence housing prices in San Antonio.
Strategies for Improvement
Texas faces significant challenges in ensuring affordable housing for its diverse population, but several strategies could help mitigate the issues:
Policy Adjustments for Affordability
State and local governments should consider implementing policies that encourage the development of more affordable housing options. This could include:
- Offering incentives to developers who include affordable units in their projects
- Streamlining the permitting process for affordable housing developments
- Allowing for higher-density development in certain areas to increase the housing supply
- Providing tax breaks or subsidies for low-income renters and homebuyers
Innovative Housing Solutions
To address Texas’ unique geographical and economic landscape, innovative housing solutions should be explored:
- Encouraging the development of mixed-use, walkable communities near job centers to reduce transportation costs
- Promoting the use of alternative building materials and construction methods to lower development costs
- Exploring the potential of tiny homes, co-living spaces, and other non-traditional housing options
- Partnering with major employers to develop workforce housing near employment hubs
- Adapting housing designs to withstand better the state’s varied climate conditions, from hurricanes to heatwaves
Conclusion
Texas’ housing affordability is a multifaceted issue deeply influenced by the state’s diverse geography, economic landscape, and urban development patterns.
By understanding the intricate interplay of factors like income disparities, physical barriers, and land use policies, we can work towards crafting effective solutions to ensure all Texans have access to affordable homes.
As the Lone Star State continues to grow and evolve, policymakers, developers, and communities must collaborate to implement innovative strategies tailored to each region’s unique needs.
From incentivizing affordable housing development to exploring alternative living options, Texas has the opportunity to create a more equitable and accessible housing market.
The path forward may be challenging, but with determination and ingenuity, we can build a future where every Texan can find a place to call home.